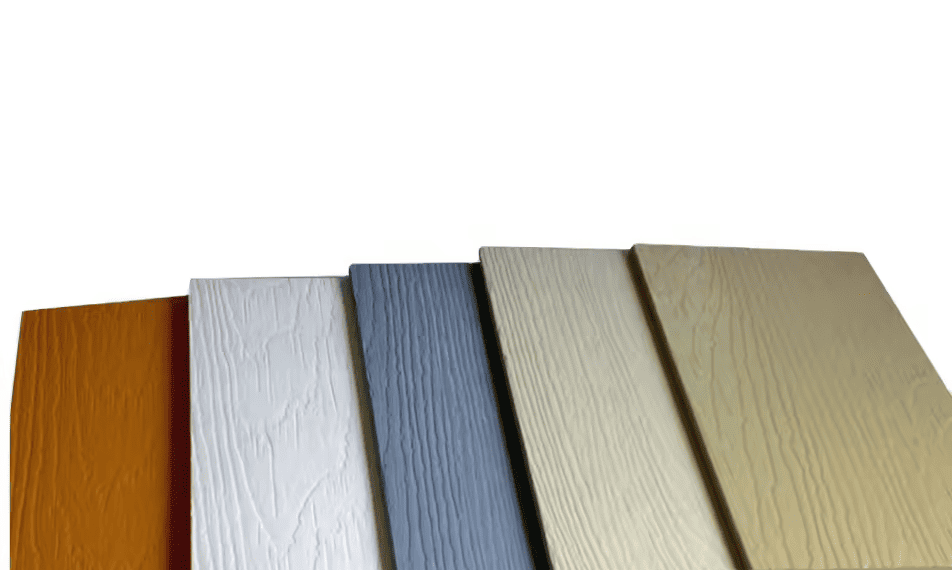
What is Another Name for Cement Board Siding?
Cement board siding is also known as fiber cement siding, cement fiberboard, or cementitious siding, with various industry-leading products all referring to engineered composite materials combining Portland cement with cellulose fibers for exterior wall applications.
Fiber cement siding represents the most common alternative name describing cellulose fiber reinforcement in cement matrix composition. Cementitious siding indicates cement-based materials used for exterior applications. Well-known industry brands have become generic references in the construction industry. Cement fiberboard emphasizes the composite nature of fiber-reinforced cement. Regional terminology varies with local market preferences but describes identical products with similar performance characteristics.
From my extensive experience in cement board manufacturing, I've observed that terminology confusion often leads to specification errors and missed opportunities for optimal product selection in exterior applications.
Is Cement Siding the Same as Stucco?
No, cement siding and stucco are different exterior systems - cement siding consists of pre-manufactured fiber cement panels or planks installed mechanically, while stucco is a wet-applied coating system of cement, sand, and lime troweled directly onto building surfaces, with different installation methods, appearance, and maintenance requirements.
Cement siding uses pre-manufactured panels installed with mechanical fasteners over structural sheathing creating distinct joint lines. Stucco applies wet cement mixture directly to wall surfaces creating continuous monolithic finish without visible seams. Installation methods differ completely with siding requiring carpentry skills while stucco needs plastering expertise. Maintenance approaches vary with siding allowing individual panel replacement while stucco requires patching techniques. Cost structures differ with siding having higher material costs but lower skilled labor requirements.
System Comparison Analysis
Fundamental differences between cement siding and stucco affect performance and application suitability.
| System Characteristic | Cement Siding | Stucco | Performance Impact | Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Mechanical fastening | Wet application | Speed vs skill | Labor availability |
| Joint Treatment | Visible seams | Continuous surface | Aesthetic preference | Design intent |
| Repair Approach | Panel replacement | Patch application | Maintenance ease | Long-term costs |
| Texture Options | Factory applied | Field customizable | Consistency vs variety | Quality control |
| Weather Resistance | Mechanical drainage | Monolithic barrier | Water management | Climate considerations |
Mechanical installation gives cement siding advantages in speed and weather-independent application.
Performance Characteristics
Different performance attributes make each system suitable for specific applications and climates.
| Performance Factor | Cement Siding | Stucco | Durability Rating | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Management | Drainage system | Barrier approach | Excellent vs Good | Low vs Moderate |
| Crack Resistance | Joint accommodation | Monolithic expansion | Superior vs Fair | Panel replacement vs patching |
| Fire Resistance | Class A rating | Class A rating | Equal performance | Similar standards |
| Impact Resistance | High strength | Variable thickness | Good vs Fair | Individual assessment |
| UV Stability | Factory finish | Field application | Consistent vs Variable | Predictable vs site-dependent |
Water management systems in cement siding provide superior long-term performance.
Cost Analysis Comparison
Total cost considerations include materials, installation, and long-term maintenance factors.
| Cost Component | Cement Siding | Stucco | Cost Difference | Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Costs | $3-8/sq ft | $2-5/sq ft | Higher initial | Predictable quality |
| Installation Labor | $2-4/sq ft | $3-6/sq ft | Lower labor | Faster installation |
| Total Installed Cost | $5-12/sq ft | $5-11/sq ft | Comparable range | Different value drivers |
| Maintenance Costs | $0.10-0.20/sq ft/year | $0.20-0.40/sq ft/year | Lower long-term | Reduced service needs |
| Lifespan | 30-50 years | 20-30 years | Extended duration | Better investment |
Lower maintenance costs make cement siding economically attractive over building lifecycle.
What Are the Three Types of Siding?
The three main siding types are natural material siding including wood and stone, manufactured panel siding such as vinyl and fiber cement, and applied coating systems like stucco and EIFS, each offering distinct installation methods, performance characteristics, and aesthetic possibilities for exterior wall applications.
Natural material siding includes wood clapboard, cedar shakes, stone veneer providing authentic textures with traditional installation methods. Manufactured panel siding encompasses vinyl, aluminum, fiber cement, composite materials offering consistent quality and standardized installation. Applied coating systems include stucco, EIFS, synthetic finishes creating continuous surfaces through wet application processes. Each category serves different performance priorities including cost, maintenance, appearance, durability. Selection depends on climate conditions, budget constraints, aesthetic preferences.
Natural Material Siding
Traditional natural materials provide authentic appearance with varying maintenance and cost requirements.
| Natural Material | Installation Method | Maintenance Level | Cost Range | Lifespan | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood Clapboard | Nail fastening | High | $6-12/sq ft | 20-30 years | Renewable resource |
| Cedar Shakes | Overlap installation | High | $8-15/sq ft | 25-40 years | Natural preservation |
| Stone Veneer | Mortar application | Low | $15-30/sq ft | 50+ years | Permanent material |
| Brick Veneer | Masonry installation | Low | $12-25/sq ft | 50+ years | Durable/recyclable |
| Log Siding | Tongue/groove | High | $10-20/sq ft | 30-50 years | Traditional aesthetic |
Stone and brick veneer offer the lowest maintenance among natural materials.
Manufactured Panel Systems
Engineered siding products provide consistent quality and standardized installation procedures.
| Panel Type | Material Composition | Installation Speed | Color Options | Weather Resistance | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding | PVC plastic | Fast | Limited/fade prone | Good | High value |
| Aluminum Siding | Coated metal | Fast | Factory applied | Excellent | Moderate value |
| Fiber Cement | Cement/fiber composite | Moderate | Paintable/pre-finished | Excellent | Good value |
| Composite Siding | Wood fiber/resin | Moderate | Pre-finished | Very good | Premium pricing |
| Steel Siding | Galvanized steel | Fast | Factory applied | Excellent | Moderate value |
Fiber cement siding provides optimal balance of performance and cost effectiveness.
Applied Coating Systems
Wet-applied exterior finishes create continuous surfaces with customizable textures and appearances.
| Coating System | Base Requirements | Texture Options | Repair Method | Climate Suitability | Installation Skill |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Stucco | Wire lath/sheathing | Hand troweled | Patch/blend | Dry climates | High skill |
| EIFS | Foam insulation | Synthetic textures | System repair | All climates | Specialized |
| Acrylic Finish | Prepared substrate | Sprayed/rolled | Spot repair | Moderate climates | Moderate skill |
| Cement Render | Block/concrete | Trowel applied | Patch application | All climates | High skill |
| Synthetic Stucco | Various substrates | Textured options | Section repair | Climate dependent | Moderate skill |
EIFS systems provide superior insulation value with applied coating benefits.
What is the Most Common Siding on a House?
Vinyl siding is the most common house siding in North America, used on approximately 35-40% of residential construction, followed by fiber cement at 15-20%, wood at 10-15%, and aluminum at 8-12%, with regional variations based on climate, cost factors, and local building traditions.
Vinyl siding dominates due to low cost, easy maintenance and wide availability with color options and texture varieties. Fiber cement shows rapid growth as premium alternative offering superior durability and fire resistance. Regional preferences vary with wood popular in Pacific Northwest, stucco common in Southwest, brick prevalent in Southeast. New construction increasingly specifies fiber cement while renovation projects often choose vinyl for cost considerations. Market trends show declining aluminum use and growing composite adoption.
Market Share Analysis
Siding material usage varies by region, construction type, and price point considerations.
| Siding Type | National Market Share | New Construction | Renovation Market | Growth Trend | Regional Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 35-40% | 30% | 50% | Stable | Midwest/Northeast |
| Fiber Cement | 15-20% | 25% | 10% | Growing | All regions |
| Wood | 10-15% | 8% | 18% | Declining | Pacific Northwest |
| Aluminum | 8-12% | 5% | 15% | Declining | Northern climates |
| Stucco/EIFS | 12-15% | 20% | 5% | Stable | Southwest/Southeast |
Fiber cement shows strongest growth in new construction applications.
Cost-Performance Analysis
Different siding materials offer varying value propositions across multiple performance criteria.
| Material | Initial Cost | Installation Cost | Maintenance Cost | Lifespan | Total Value Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Low | Low | Very Low | 20-30 years | High value |
| Fiber Cement | Medium | Medium | Low | 30-50 years | Excellent value |
| Wood | Medium-High | Medium | High | 20-30 years | Moderate value |
| Aluminum | Medium | Low | Low | 30-40 years | Good value |
| Brick/Stone | High | High | Very Low | 50+ years | Premium value |
Vinyl siding provides highest value for cost-conscious applications.
Regional Preferences
Geographic factors influence siding material selection based on climate and local building practices.
| Region | Primary Choice | Secondary Choice | Climate Factors | Local Preferences | Market Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | Vinyl | Fiber cement | Freeze/thaw cycles | Traditional aesthetics | Cost/maintenance |
| Southeast | Brick/Stucco | Vinyl | High humidity | Hurricane resistance | Durability |
| Midwest | Vinyl | Aluminum | Temperature extremes | Practical approach | Value/performance |
| Southwest | Stucco | Fiber cement | Arid climate | Regional tradition | Aesthetic/climate |
| Pacific Northwest | Wood | Fiber cement | High moisture | Natural materials | Environmental values |
Regional climate conditions significantly influence optimal siding material selection.
Conclusion
Cement board siding is also known as fiber cement siding, cement fiberboard, or cementitious siding with various industry brands representing composite materials combining Portland cement with cellulose fibers. Cement siding differs from stucco as pre-manufactured panels with mechanical installation versus wet-applied coating systems troweled directly onto surfaces. Three main siding types include natural materials like wood and stone, manufactured panels such as vinyl and fiber cement, and applied coating systems including stucco and EIFS. Vinyl siding represents the most common house siding at 35-40% market share due to low cost and easy maintenance, followed by fiber cement showing rapid growth in new construction applications. Success in siding selection requires understanding that terminology confusion affects specification accuracy, system differences impact installation and maintenance approaches, material categories serve different performance priorities, and market preferences vary by region and application type, making proper material selection critical for achieving optimal performance, cost effectiveness, and aesthetic satisfaction in exterior wall systems.